Blar i tittel Artikler, rapporter og annet (fysikk og teknologi)
Viser treff 375-394 av 942
-
Impacts of snow data and processing methods on the interpretation of long-term changes in Baffin Bay early spring sea ice thickness
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2021-10-21)In the Arctic, multi-year sea ice is being rapidly replaced by seasonal sea ice. Baffin Bay, situated between Greenland and Canada, is part of the seasonal ice zone. In this study, we present a long-term multi-mission assessment (2003–2020) of spring sea ice thickness in Baffin Bay from satellite altimetry and sea ice charts. Sea ice thickness within Baffin Bay is calculated from Envisat, ... -
Improved Arctic Sea Ice Freeboard Retrieval From Satellite Altimetry Using Optimized Sea Surface Decorrelation Scales
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2021-11-18)A growing number of studies are concluding that the resilience of the Arctic sea ice cover in a warming climate is essentially controlled by its thickness. Satellite radar and laser altimeters have allowed us to routinely monitor sea ice thickness across most of the Arctic Ocean for several decades. However, a key uncertainty remaining in the sea ice thickness retrieval is the error on the sea surface ... -
Improved LLM Methods Using Linear Regression
(Journal article; Peer reviewed, 2017-12-04)This paper is focused on investigations of the improved correction of the effect of variation in incidence angle on ScanSAR data. Conventional correction methods (such as LLM, locally linear mapping) typically assume that each target class has a similarity distribution in the middle of the image. The objectives of this study are to extend the correction algorithm to full swath width without any ... -
An improved spatial and temporal reflectance unmixing model to synthesize time series of landsat-like images
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2018-08-31)The trade-off between spatial and temporal resolution limits the acquisition of dense time series of Landsat images, and limits the ability to properly monitor land surface dynamics in time. Spatiotemporal image fusion methods provide a cost-efficient alternative to generate dense time series of Landsat-like images for applications that require both high spatial and temporal resolution images. The ... -
An Improved Spatial and Temporal Reflectance Unmixing Model to Synthesize Time Series of Landsat-Like Images
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2018-08-31)The trade-off between spatial and temporal resolution limits the acquisition of dense time series of Landsat images, and limits the ability to properly monitor land surface dynamics in time. Spatiotemporal image fusion methods provide a cost-efficient alternative to generate dense time series of Landsat-like images for applications that require both high spatial and temporal resolution images. The ... -
Improvements in September Arctic Sea Ice Predictions Via Assimilation of Summer CryoSat-2 Sea Ice Thickness Observations
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2023-12-15)Because of a spring predictability barrier, the seasonal forecast skill of Arctic summer sea ice is limited by the availability of melt-season sea ice thickness (SIT) observations. The first year-round SIT observations, retrieved from CryoSat-2 from 2011 to 2020, are assimilated into the GFDL ocean–sea ice model. The model's SIT anomaly field is brought into significantly better agreement with the ... -
Improving Chlorophyll-a Estimation from Sentinel-2 (MSI) in the Barents Sea using Machine Learning
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2021-04-22)This article addresses methodologies for remote sensing of ocean Chlorophyll-a (Chl-a), with emphasis on the Barents Sea. We aim at improving the monitoring capacity by integrating in situ Chl-a observations and optical remote sensing to locally train machine learning (ML) models. For this purpose, in situ measurements of Chl-a ranging from 0.014–10.81 mg/m <sup>3</sup> , collected for the years ... -
Improving Doppler frequency estimation from Envisat data
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2014-11-06)This paper shows that Envisat ASAR data are degraded by a small periodic variation in gain between internal calibration cycles of the antenna, which introduces a significant bias when we try to estimate line-of-sight surface velocities from the estimated Doppler frequency shifts. We investigate the impact of the gain problems on the derived surface velocity product and propose a simple correction ... -
Improving Doppler frequency estimation from Envisat data
(Conference object; Konferansebidrag, 2014) -
Improving satellite-based monitoring of the polar regions: Identification of research and capacity gaps
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2023-02-17)We present a comprehensive review of the current status of remotely sensed and in situ sea ice, ocean, and land parameters acquired over the Arctic and Antarctic and identify current data gaps through comparison with the portfolio of products provided by Copernicus services. While we include several land parameters, the focus of our review is on the marine sector. The analysis is facilitated by the ... -
Improving sea surface temperature in a regional ocean model through refined sea surface temperature assimilation
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2023-05-26)Infrared (IR) and passive microwave (PMW) satellite sea surface temperature (SST) retrievals are valuable to assimilate into high-resolution regional ocean forecast models. Still, there are issues related to these SSTs that need to be addressed to achieve improved ocean forecasts. Firstly, satellite SST products tend to be biased. Assimilating SSTs from different providers can thus cause the ocean ... -
Impulse-driven oscillations of the near-Earth's magnetosphere
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2022-11-09)It is argued that a simple model based on magnetic image arguments suffices to give a convincing insight into both the basic static as well as some transient dynamic properties of the near-Earth's magnetosphere, particularly accounting for damped oscillations being excited in response to impulsive perturbations. The parameter variations of the frequency are given. Qualitative results can also be ... -
In-Silico Evaluation of Glucose Regulation Using Policy Gradient Reinforcement Learning for Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2020-09-11)In this paper, we test and evaluate policy gradient reinforcement learning for automated blood glucose control in patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Recent research has shown that reinforcement learning is a promising approach to accommodate the need for individualized blood glucose level control algorithms. The motivation for using policy gradient algorithms comes from the fact that adaptively ... -
Incident Angle Dependence of Sentinel-1 Texture Features for Sea Ice Classification
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2021-02-04)Robust and reliable classification of sea ice types in synthetic aperture radar (SAR) images is needed for various operational and environmental applications. Previous studies have investigated the class-dependent decrease in SAR backscatter intensity with incident angle (IA); others have shown the potential of textural information to improve automated image classification. In this work, we investigate ... -
Incorporating Incidence Angle Variation into Sar Image Segmentation
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2018-11-05)We present a new approach for incorporating incidence angle derived synthetic aperture radar (SAR) brightness variation directly into SAR image analysis. This approach is unique in that the incidence angle dependency is modeled explicitly into the probability density function rather than an image-wide pre-processing `correction'. It can then be used for supervised and unsupervised image analysis, ... -
Incorporating Incidence Angle Variation into Sar Image Segmentation
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2018)We present a new approach for incorporating incidence angle derived synthetic aperture radar (SAR) brightness variation directly into SAR image analysis. This approach is unique in that the incidence angle dependency is modeled explicitly into the probability density function rather than an image-wide pre-processing ‘correction’. It can then be used for supervised and unsupervised image analysis, ... -
Increasing Multiyear Sea Ice Loss in the Beaufort Sea: A New Export Pathway for the Diminishing Multiyear Ice Cover of the Arctic Ocean
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2022-05-16)Historically, multiyear sea ice (MYI) covered a majority of the Arctic and circulated through the Beaufort Gyre for years. However, increased ice melt in the Beaufort Sea during the early 2000s was proposed to have severed this circulation. Constructing a regional MYI budget from 1997 to 2021 reveals that MYI import into the Beaufort Sea has increased year-round, yet less MYI now survives through ... -
Inferring neutral winds in the ionospheric transition region from atmospheric-gravity-wave traveling-ionospheric-disturbance (AGW-TID) observations with the EISCAT VHF radar and the Nordic Meteor Radar Cluster
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2023-10-18)Atmospheric gravity waves and traveling ionospheric disturbances can be observed in the neutral atmosphere and the ionosphere at a wide range of spatial and temporal scales. Especially at medium scales, these oscillations are often not resolved in general circulation models and are parameterized. We show that ionospheric disturbances forced by upward-propagating atmospheric gravity waves can be ... -
Inferring the Dielectric Properties of Oil Slick from Multifrequency SAR imagery via a Polarimetric Two-Scale Model
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel, 2021-04)We apply a polarimetric two-scale model to multifrequency synthetic aperture radar imagery of verified oil slicks measured by DLRs F-SAR instrument, which can acquire high spatial resolution and high signal-to-noise data. The purpose, is to determine the permittivity of the scattering surface via an inversion procedure. The ocean surface is modelled as an ensemble of randomly orientated, tilted ... -
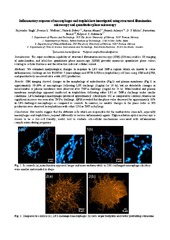
Inflammatory response of macrophages and trophoblasts investigated using structured illumination microscopy and quantitative phase microscopy
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2017-09)<i>Introduction</i>: The super-resolution capability of structured illumination microscopy (SIM) (100 nm) enables 3D imaging of mitochondria, and label-free quantitative phase microscopy (QPM) provides nanoscale quantitative phase values relating to cellular thickness and the refractive index of cellular content.


 English
English norsk
norsk