| dc.contributor.author | Knies, Jochen | |
| dc.contributor.author | Pathirana, Irene Dorothea | |
| dc.contributor.author | Cabedo-Sanz, Patricia | |
| dc.contributor.author | Banica, Ana | |
| dc.contributor.author | Fabian, Karl | |
| dc.contributor.author | Rasmussen, Tine Lander | |
| dc.contributor.author | Forwick, Matthias | |
| dc.contributor.author | Belt, Simon T. | |
| dc.date.accessioned | 2018-03-26T09:54:47Z | |
| dc.date.available | 2018-03-26T09:54:47Z | |
| dc.date.issued | 2016-12-23 | |
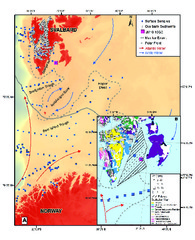
| dc.description.abstract | The production of high-salinity brines during sea-ice freezing in circum-arctic coastal polynyas is thought to be part of northern deep water formation as it supplies additional dense waters to the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation system. To better predict the effect of possible future summer ice-free conditions in the Arctic Ocean on global climate, it is important to improve our understanding of how climate change has affected sea-ice and brine formation, and thus finally dense water formation during the past. Here, we show temporal coherence between sea-ice conditions in a key Arctic polynya (Storfjorden, Svalbard) and patterns of deep water convection in the neighbouring Nordic Seas over the last 6500 years. A period of frequent sea-ice melting and freezing between 6.5 and 2.8 ka BP coincided with enhanced deep water renewal in the Nordic Seas. Near-permanent sea-ice cover and low brine rejection after 2.8 ka BP likely reduced the overflow of high-salinity shelf waters, concomitant with a gradual slow down of deep water convection in the Nordic Seas, which occurred along with a regional expansion in sea-ice and surface water freshening. The Storfjorden polynya sea-ice factory restarted at ~0.5 ka BP, coincident with renewed deep water penetration to the Arctic and climate amelioration over Svalbard. The identified synergy between Arctic polynya sea-ice conditions and deep water convection during the present interglacial is an indication of the potential consequences for ocean ventilation during states with permanent sea-ice cover or future Arctic ice-free conditions. | en_US |
| dc.description | The final publication is available at <a href=http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s41063-016-0027-y> https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs41063-016-0027-y </a>. | en_US |
| dc.identifier.citation | Knies, J., Pathirana, I., Cabedo-Sanz, P., Banica, A., Fabian, K., Rasmussen, T. L. ... Belt, S. T. (2017). Sea-ice dynamics in an Arctic coastal polynya during the past 6500 years. Arktos. 3(1) | en_US |
| dc.identifier.cristinID | FRIDAID 1418973 | |
| dc.identifier.doi | 10.1007/s41063-016-0027-y | |
| dc.identifier.issn | 2364-9453 | |
| dc.identifier.issn | 2364-9461 | |
| dc.identifier.uri | https://hdl.handle.net/10037/12440 | |
| dc.language.iso | eng | en_US |
| dc.publisher | Springer | en_US |
| dc.relation.journal | Arktos | |
| dc.relation.projectID | info:eu-repo/grantAgreement/RCN/SFF/223259/NORWAY/Centre for Arctic Gas Hydrate, Environment and Climate/CAGE/ | en_US |
| dc.relation.projectID | info:eu-repo/grantAgreement/EC/ FP7-PEOPLE/238111/EU/THE CHANGING ARCTIC AND SUB-ARCTIC ENVIRONMENT: A RESEARCH AND TRAINING PROGRAMME ON MARINE BIOTIC INDICATORS OF RECENT CLIMATE CHANGES IN THE HIGH LATITUDES OF THE NORTH ATLANTIC// | en_US |
| dc.rights.accessRights | openAccess | en_US |
| dc.subject | Arctic | en_US |
| dc.subject | Storfjorden | en_US |
| dc.subject | Polynya | en_US |
| dc.subject | Holocene | en_US |
| dc.subject | Sea ice | en_US |
| dc.subject | VDP::Matematikk og Naturvitenskap: 400::Geofag: 450 | en_US |
| dc.subject | VDP::Mathematics and natural science: 400::Geosciences: 450 | en_US |
| dc.title | Sea-ice dynamics in an Arctic coastal polynya during the past 6500 years | en_US |
| dc.type | Journal article | en_US |
| dc.type | Tidsskriftartikkel | en_US |
| dc.type | Peer reviewed | en_US |


 English
English norsk
norsk