Artikler, rapporter og annet (arktisk og marin biologi): Nye registreringer
Viser treff 721-740 av 1637
-
Shallow-Water Scavengers of Polar Night and Day – An Arctic Time-Lapse Photography Study
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2021-05-24)Until recently, polar night constituted truly a “mare incognitum” of our times. Yet, the first records from this very little-explored period showcased a surprisingly rich and active ecosystem. This investigation aims to reveal the level of scavenger activity during both Arctic polar night and day. It compares the shallow-water scavenging fauna observed during two contrasting seasons (winter vs. ... -
A marine zooplankton community vertically structured by light across diel to interannual timescales
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2021-02-24)The predation risk of many aquatic taxa is dominated by visually searching predators, commonly a function of ambient light. Several studies propose that changes in visual predation will become a major climate-change impact on polar marine ecosystems. The High Arctic experiences extreme seasonality in the light environment, from 24 h light to 24 h darkness, and therefore provides a natural laboratory ... -
The occurrence of Nematoda in coastal sea ice on Svalbard (European Arctic) determined with the 18S small subunit rRNA gene
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2021-05-06)Understanding the diversity and functioning of Arctic sea ice ecosystems is vital to evaluate and predict the impact of current and future climate change. In the microscopic communities inhabiting the brine channels inside sea ice, nematodes often dominate numerically and act as bacterivores and herbivores. Despite nematodes great abundances and known ecological roles, molecular tools have not been ... -
Bearded seal (Erignathus barbatus) vocalizations across seasons and habitat types in Svalbard, Norway
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2021-05-17)Male bearded seals (Erignathus barbatus) use vocal displays to attract females and to compete with other males during the mating season. This makes it possible to monitor breeding populations of this species using passive acoustic monitoring (PAM). This study analysed year-round acoustic data records from AURAL instruments in Svalbard (Norway) to investigate seasonal variation in the acoustic presence ... -
SIOS’s Earth Observation (EO), Remote Sensing (RS), and operational activities in response to COVID-19
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2021-02-15)Svalbard Integrated Arctic Earth Observing System (SIOS) is an international partnership of research institutions studying the environment and climate in and around Svalbard. SIOS is developing an efficient observing system, where researchers share technology, experience, and data, work together to close knowledge gaps, and decrease the environmental footprint of science. SIOS maintains and facilitates ... -
Iterative model predictions for wildlife populations impacted by rapid climate change
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2021-01-14)To improve understanding and management of the consequences of current rapid environmental change, ecologists advocate using long-term monitoring data series to generate iterative near-term predictions of ecosystem responses. This approach allows scientific evidence to increase rapidly and management strategies to be tailored simultaneously. Iterative near-term forecasting may therefore be particularly ... -
Modeling silicate–nitrate–ammonium co-limitation of algal growth and the importance of bacterial remineralization based on an experimental Arctic coastal spring bloom culture study
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2021-03-11)Arctic coastal ecosystems are rapidly changing due to climate warming. This makes modeling their productivity crucially important to better understand future changes. System primary production in these systems is highest during the pronounced spring bloom, typically dominated by diatoms. Eventually the spring blooms terminate due to silicon or nitrogen limitation. Bacteria can play an important role ... -
Terrestrial Inputs Shape Coastal Bacterial and Archaeal Communities in a High Arctic Fjord (Isfjorden, Svalbard)
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2021-02-26)The Arctic is experiencing dramatic changes including increases in precipitation, glacial melt, and permafrost thaw, resulting in increasing freshwater runoff to coastal waters. During the melt season, terrestrial runoff delivers carbon- and nutrient-rich freshwater to Arctic coastal waters, with unknown consequences for the microbial communities that play a key role in determining the cycling and ... -
Analysis across diverse fish species highlights no conserved transcriptome signature for proactive behaviour
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2021-01-07)<p>Background: Consistent individual differences in behaviour, known as animal personalities, have been demonstrated within and across species. In fish, studies applying an animal personality approach have been used to resolve variation in physiological and molecular data suggesting a linkage, genotype-phenotype, between behaviour and transcriptome regulation. In this study, using three fish species ... -
Influence of Arctic light conditions on crop production and quality
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2021-04-10)The natural light conditions above the Arctic Circle are unique in terms of annual variation creating special growth conditions for crop production. These include low solar elevations, very long daily photosynthetic light periods, midnight sun/absence of dark nights, and altered spectral distribution depending on solar elevation. All these factors are known to affect the growth and the metabolism ... -
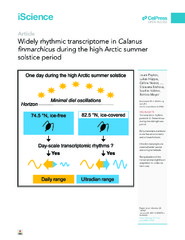
Widely rhythmic transcriptome in Calanus finmarchicus during the high Arctic summer solstice period
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2020-12-10)Solar light/dark cycles and seasonal photoperiods underpin daily and annual rhythms of life on Earth. Yet, the Arctic is characterized by several months of permanent illumination (“midnight sun”). To determine the persistence of 24h rhythms during the midnight sun, we investigated transcriptomic dynamics in the copepod <i>Calanus finmarchicus</i> during the summer solstice period in the Arctic, with ... -
Quantifying the consequence of applying conservative assumptions in the assessment of oil spill effects on polar cod (Boreogadus saida) populations
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2021-02-23)In order to assess the potential impact from oil spills and decide the optimal response actions, prediction of population level effects of key resources is crucial. These assessments are usually based on acute toxicity data combined with precautionary assumptions because chronic data are often lacking. To better understand the consequences of applying precautionary approaches, two approaches for ... -
Body Temperature and Activity Rhythms Under Different Photoperiods in High Arctic Svalbard ptarmigan (Lagopus muta hyperborea)
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2021-03-08)Organisms use circadian rhythms to anticipate and exploit daily environmental oscillations. While circadian rhythms are of clear importance for inhabitants of tropic and temperate latitudes, its role for permanent residents of the polar regions is less well understood. The high Arctic Svalbard ptarmigan shows behavioral rhythmicity in presence of light-dark cycles but is arrhythmic during the polar ... -
Site-specific responses of fungal and bacterial abundances to experimental warming in litter and soil across arctic and alpine tundra
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2021-04-01)Vegetation change of the Arctic tundra due to global warming is a well-known process, but the implication for the belowground microbial communities, key in nutrient cycling and decomposition, is poorly understood. We characterized the fungal and bacterial abundances in litter and soil layers across 16 warming experimental sites at 12 circumpolar locations. We investigated the relationship between ... -
The hidden influence of large particles on ocean colour
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2021-02-17)Optical constituents in the ocean are often categorized as water, phytoplankton, sediments and dissolved matter. However, the optical properties of seawater are influenced, to some degree, by scattering and absorption by all particles in the water column. Here we assess the relevant size ranges for determining the optical properties of the ocean. We present a theoretical basis supporting the hypothesis ... -
Redefining the oceanic distribution of Atlantic salmon
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2021-06-10)Determining the mechanisms driving range-wide reductions in Atlantic salmon marine survival is hindered by an insufcient understanding of their oceanic ecology and distribution. We attached 204 pop-up satellite archival tags to post-spawned salmon when they migrated to the ocean from seven European areas and maiden North American salmon captured at sea at West Greenland. Individuals migrated ... -
Early spring subglacial discharge plumes fuel under-ice primary production at a Svalbard tidewater glacier
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2021-04-27)Subglacial upwelling of nutrient-rich bottom water is known to sustain elevated summer primary production in tidewater-glacier-influenced fjord systems. However, the importance of subglacial upwelling during the early spring season has not been considered yet. We hypothesized that subglacial discharge under sea ice is present in early spring and that its flux is sufficient to increase phytoplankton ... -
Dense mesopelagic sound scattering layer and vertical segregation of pelagic organisms at the Arctic-Atlantic gateway during the midnight sun
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2021-05-18)Changes in vertical and spatial distributions of zooplankton and small pelagic fish impact the biological carbon pump and the distribution of larger piscivorous fish and marine mammal species. However, their distribution and abundance remain poorly documented at high latitudes because of the difficulties inherent to sampling relatively fast-moving organisms in ice-covered waters. This study documents ... -
Summer and winter MgCO3 levels in the skeletons of Arctic bryozoans
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2020-10-02)<p>In the Arctic, seasonal patterns in seawater biochemical conditions are shaped by physical, chemical, and biological processes related to the alternation of seasons, i.e. winter polar night and summer midnight sun. In summertime, CO<sub>2</sub> concentration is driven by photosynthetic activity of autotrophs which raises seawater pH and carbonate saturation state (Ω). In addition, restriction of ... -
Caligus elongatus and other sea lice of the genus Caligus as parasites of farmed salmonids: A review
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2020-02-24)This review was prompted by reports of unusually large numbers of sea lice tentatively identified as <i>Caligus elongatus</i> infesting farmed salmon in northern Norway. Following a brief introduction to the sea lice problem in salmonid aquaculture, the review is divided into a further eight sections. The first is a review of existing information on the life cycle and behaviour of <i>Caligus</i> ...


 English
English norsk
norsk