Blar i forfatter Artikler, rapporter og annet (matematikk og statistikk) "Fredriksen, Hege-Beate"
-
Are there multiple scaling regimes in Holocene temperature records?
Nilsen, Tine; Rypdal, Kristoffer; Fredriksen, Hege-Beate (Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2016-04-28)In this article it is discussed how temperature variability on centennial timescales and longer can be described in a simplistic way. By analysing the scaling in late Holocene temperature reconstructions and longer temperature records from Greenland and Antarctic ice cores, we find that the choice of model depends heavily on the data material and timescale one chooses to emphasize. Ignoring data ... -
Are there multiple scaling regimes in Holocene temperature records?
Nilsen, Tine; Rypdal, Kristoffer; Fredriksen, Hege-Beate (Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel, 2015-07-17)The concept of multiple scaling regimes in temperature time series is examined, with emphasis on the question whether or not a mono-scaling model can be rejected from the data at hand. A model with only one regime is simpler and is preferred if this 5 explains the observed variability. Our analysis of spectra from reconstructed air temperature from Greenland and Antarctica ice cores shows that ... -
Eilertsen-bløffen
Fredriksen, Hege-Beate (Chronicle; Kronikk, 2015-06-27)Kristian Eilertsen i Troms FRP prøver i Nordlys 24. juni febrilsk å justere fakta etter sine politiske oppfatninger – og ikke motsatt – når han oppdager at seriøse argumenter mot menneskeskapte klimaendringer forsvinner som dugg for solen. Han er heldigvis på kollisjonskurs med FRPs egen olje- og energiminister, som sammen med direktøreni Statoil har erklært at det skjer en menneskeskapt global ... -
Emergent Scale Invariance and Climate Sensitivity
Rypdal, Martin Wibe; Fredriksen, Hege-Beate; Myrvoll-Nilsen, Eirik; Rypdal, Kristoffer; Sørbye, Sigrunn Holbæk (Journal article; Peer reviewed, 2018-11-28)Earth’s global surface temperature shows variability on an extended range of temporal scales and satisfies an emergent scaling symmetry. Recent studies indicate that scale invariance is not only a feature of the observed temperature fluctuations, but an inherent property of the temperature response to radiative forcing, and a principle that links the fast and slow climate responses. It provides a ... -
En investering i tvil
Fredriksen, Hege-Beate (Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel, 2015-07-30)Ifølge Ole Henrik Ellestads innlegg i Nordlys 20. juli er alle modeller som ikke stemmer overens med observasjoner gale. Det kan man godt si, men det betyr at alle modeller er gale. En modell er en forenklet versjon av virkeligheten, og vil alltid avvike noe fra observasjonene. Man lærer likevel mye av å bruke modeller.Klimamodellene er gode på å forutsi forventet temperaturrespons på eksterne ... -
Estimating Remaining Carbon Budgets Using Temperature Responses Informed by CMIP6
Rypdal, Martin Wibe; Boers, Niklas; Fredriksen, Hege-Beate; Eiselt, Kai-Uwe; Johansen, Andreas; Martinsen, Andreas Rostrup; Mentzoni, Endre Falck; Graversen, Rune; Rypdal, Kristoffer (Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2021-07-12)A remaining carbon budget (RCB) estimates how much CO2 we can emit and still reach a specific temperature target. The RCB concept is attractive since it easily communicates to the public and policymakers, but RCBs are also subject to uncertainties. The expected warming levels for a given carbon budget has a wide uncertainty range, which increases with less ambitious targets, i.e., with higher CO2 ... -
Is there a break in scaling on centennial time scales in Holocene temperature records?
Nilsen, Tine; Rypdal, Kristoffer; Fredriksen, Hege-Beate (Conference object; Konferansebidrag, 2017) -
Long-range persistence in global surface temperatures explained by linear multibox energy balance models
Fredriksen, Hege-Beate; Rypdal, Martin Wibe (Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2017-09-15)The temporal fluctuations in global mean surface temperature are an example of a geophysical quantity that can be described using the notions of long-range persistence and scale invariance/scaling, but this description has suffered from lack of a generally accepted physical explanation. Processes with these statistical signatures can arise from nonlinear effects, for instance, through cascade-like ... -
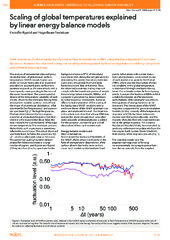
Scaling of global temperatures explained by linear energy balance models
Rypdal, Kristoffer; Fredriksen, Hege-Beate (Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2017-12)<i>Introduction</i>: Scale invariance of natural variability of global surface temperatures is often interpreted as a signature of nonlinear dynamics. However, the observed scaling can be adequately explained by linear energy balance involving subsystems with different response times. -
Spatiotemporal Long-Range Persistence in Earth’s Temperature Field: Analysis of Stochastic-Diffusive Energy Balance Models
Rypdal, Kristoffer; Rypdal, Martin Wibe; Fredriksen, Hege-Beate (Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2015-11-01)A two-dimensional stochastic–diffusive energy balance model (EBM) formulated on a sphere by G. R. North et al. is explored and generalized. Instantaneous and frequency-dependent spatial autocorrelation functions and local temporal power spectral densities are computed for local sites and for spatially averaged surface temperature signals up to the global scale. On time scales up to the relaxation ... -
Spectral characteristics of instrumental and climate model surface temperatures
Fredriksen, Hege-Beate; Rypdal, Kristoffer (Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2016-02-05)The spatiotemporal temperature variability for several gridded instrumental and general circulation climate model data is characterized, contrasting power spectra of local and global temperatures, land and sea temperatures, and temperatures of different regions. There is generally a high degree of agreement between the spectral characteristics of instrumental and climate model data. All but the ... -
Statistical estimation of global surface temperature response to forcing under the assumption of temporal scaling
Myrvoll-Nilsen, Eirik; Sørbye, Sigrunn Holbek; Fredriksen, Hege-Beate; Rue, Håvard; Rypdal, Martin Wibe (Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2020-04-08)Reliable quantification of the global mean surface temperature (GMST) response to radiative forcing is essential for assessing the risk of dangerous anthropogenic climate change. We present the statistical foundations for an observation-based approach using a stochastic linear response model that is consistent with the long-range temporal dependence observed in global temperature variability. We ... -
Warming trends and long-range dependent climate variability since year 1900: A Bayesian approach
Myrvoll-Nilsen, Eirik; Fredriksen, Hege-Beate; Sørbye, Sigrunn Holbek; Rypdal, Martin wibe (Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2019-08-21)Temporal persistence in unforced climate variability makes detection of trends in surface temperature difficult. Part of the challenge is methodological since standard techniques assume a separation of time scales between trend and noise. In this work we present a novel Bayesian approach to trend detection under the assumption of long-range dependent natural variability, and we use estimates of ...


 English
English norsk
norsk