Blar i tittel Artikler, rapporter og annet (arktisk og marin biologi)
Viser treff 1491-1510 av 1513
-
Whirly proteins as communicators between plant organelles and the nucleus?
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2009)Whirly proteins belong to a small family of proteins with a characteristic secondary structure and a conserved DNA binding domain that is found mainly in angiosperms. At least one member of the Whirly protein family, Whirly1, is dually targeted to the nucleus and to the chloroplasts and it was shown that apart from its initially described function as a transcriptional regulator of nuclear disease ... -
Why are Svalbard Arctic foxes Brucella spp. seronegative?
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel, 2022-07-06)Arctic foxes (Vulpes lagopus) are susceptible to smooth Brucella (s-Brucella) infection and may be exposed to such bacteria through the consumption of infected marine mammals, as implied by the finding of s-Brucella antibodies in polar bears (Ursus maritimus). Arctic foxes in Svalbard have not previously been investigated for s-Brucella antibodies, but such antibodies have been detected in Arctic ... -
Why do the boreal forest ecosystems of Northwestern Europe differ from those of Western North America?
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2016-07-20)The boreal forest is one of the largest terrestrial biomes on Earth. Conifers normally dominate the tree layer across the biome, but other aspects of ecosystem structure and dynamics vary geographically. The cause of the conspicuous differences in the understory vegetation and the herbivore–predator cycles between northwestern Europe and western North America presents an enigma. Ericaceous dwarf ... -
Why don't all species overexploit?
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2021-06-14)Overexploitation of natural resources is often viewed as a problem characteristic of only the human species. However, any species could evolve a capacity to overexploit its essential resources through natural selection and competition, even to the point of resource collapse. Here, we describe the processes that potentially lead to overexploitation and synthesize what is known about overexploitation ... -
Why Rudolph's nose is red: observational study
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel, 2012-12-17)Objective To characterise the functional morphology of the nasal microcirculation in humans in comparison with reindeer as a means of testing the hypothesis that the luminous red nose of Rudolph, one of the most well known reindeer pulling Santa Claus’s sleigh, is due to the presence of a highly dense and rich nasal microcirculation.<p> <p>Design Observational study.<p> <p>Setting Tromsø, ... -
A Widely Distributed Thraustochytrid Parasite of Diatoms Isolated from the Arctic Represents a gen. and sp. nov.
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2020-04-06)A unicellular, heterotrophic, eukaryotic parasite was isolated from nearshore Arctic marine sediment in association with the diatom <i>Pleurosigma</i> sp. The parasite possessed ectoplasmic threads that could penetrate diatom frustules. Healthy and reproducing <i>Pleurosigma</i> cultures would begin to collapse within a week following the introduction of this parasite. The parasite (2–10 μm diameter) ... -
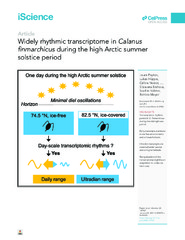
Widely rhythmic transcriptome in Calanus finmarchicus during the high Arctic summer solstice period
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2020-12-10)Solar light/dark cycles and seasonal photoperiods underpin daily and annual rhythms of life on Earth. Yet, the Arctic is characterized by several months of permanent illumination (“midnight sun”). To determine the persistence of 24h rhythms during the midnight sun, we investigated transcriptomic dynamics in the copepod <i>Calanus finmarchicus</i> during the summer solstice period in the Arctic, with ... -
Widespread soil bacterium that oxidizes atmospheric methane
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2019-04-08)Increasing atmospheric methane concentrations contribute significantly to global warming. The only known biological sink for atmospheric methane is oxidation by methane oxidizing bacteria (MOB). Due to the lack of pure cultures, the physiology and metabolic potential of MOB that oxidize atmospheric methane remains a mystery. Here, we report on isolation and characterization of a MOB that can grow ... -
Will borealization of Arctic tundra herbivore communities be driven by climate warming or vegetation change?
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2021-09-30)Poleward shifts in species distributions are expected and frequently observed with a warming climate. In Arctic ecosystems, the strong warming trends are associated with increasing greenness and shrubification. Vertebrate herbivores have the potential to limit greening and shrub advance and expansion on the tundra, posing the question of whether changes in herbivore communities could partly mediate ... -
Will borealization of Arctic tundra herbivore communities be driven by climate warming or vegetation change?
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2021-09-30)Poleward shifts in species distributions are expected and frequently observed with a warming climate. In Arctic ecosystems, the strong warming trends are associated with increasing greenness and shrubification. Vertebrate herbivores have the potential to limit greening and shrub advance and expansion on the tundra, posing the question of whether changes in herbivore communities could partly mediate ... -
Winter quarters of wetland ground beetles (Coleoptera, Carabidae) in South Scandinavia
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2011)Sites at various distances from eutrophic and mesotrophic lakes and fens on the island Öland in southern Sweden were systematically surveyed in summer (May–August) and autumn (late September–October) to elucidate the hibernation sites of wetland carabid beetles. Thirty-five of 47 wetland species were found in their winter quarters. In areas ≤50 m from the lakes and fens, the observed as well as the ... -
Winters are changing: snow effects on Arctic and alpine tundra ecosystems
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2022-02-18)Snow is an important driver of ecosystem processes in cold biomes. Snow accumulation determines ground temperature, light conditions and moisture availability during winter. It also affects the growing season’s start and end, and plant access to moisture and nutrients. Here, we review the current knowledge of the snow cover’s role for vegetation, plant-animal interactions, permafrost conditions, ... -
Within and between breeding-season changes in contaminant occurrence and body condition in the Antarctic breeding south polar skua
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2021-05-24)The Antarctic ecosystem represents a remote region far from point sources of pollution. Still, Antarctic marine predators, such as seabirds, are exposed to organohalogen contaminants (OHCs) which may induce adverse health effects. With increasing restrictions and regulations on OHCs, the levels and exposure are expected to decrease over time. We studied south polar skua (<i>Catharacta maccormicki</i>), ... -
The World's Northernmost Harbour Seal Population - How Many Are There?
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2013)This study presents the first abundance estimate for the world’s northernmost harbour seal (Phoca vitulina) population, which resides in Svalbard, Norway, based on three digital stereoscopic photographic surveys conducted in 2009 and 2010. The counts from these high resolution 3D images were combined with a novel method for estimating correction factors for animals that were in the water at the ... -
Year-round CH4 and CO2 flux dynamics in two contrasting freshwater ecosystems of the subarctic
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2017-11-21)Lakes and wetlands, common ecosystems of the high northern latitudes, exchange large amounts of the climate-forcing gases methane (CH4) and carbon dioxide (CO2) with the atmosphere. The magnitudes of these fluxes and the processes driving them are still uncertain, particularly for subarctic and Arctic lakes where direct measurements of CH4 and CO2 emissions are often of low temporal resolution and ... -
Year-round distribution of Northeast Atlantic seabird populations: applications for population management and marine spatial planning
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2021)Tracking data of marine predators are increasingly used in marine spatial management. We developed a spatial data set with estimates of the monthly distribution of 6 pelagic seabird species breeding in the Northeast Atlantic. The data set was based on year-round global location sensor (GLS) tracking data of 2356 adult seabirds from 2006−2019 from a network of seabird colonies, data describing the ... -
You are what you eat: Following fats through food chains
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel, 2010) -
Zooplankton and sediment fluxes in two contrasting fjords reveal Atlantification of the Arctic
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2021-02-04)Svalbard fjords are facing a significant increase in Atlantic water inflow, which influences all ecosystem components, thus the objective of this study was to assess how recent Atlantification impacts the functioning of zooplankton community. For this purpose, two year-round operating sediment traps and associated hydrographic instruments, providing continuous time series of zooplankton and sediment ... -
Zooplankton communities associated with new and regenerated primary production in the Atlantic inflow north of Svalbard
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2019-06-05)The Arctic Ocean is changing rapidly with respect to ice cover extent and volume, growth season duration and biological production. Zooplankton are important components in the arctic marine food web, and tightly coupled to the strong seasonality in primary production. In this study, we investigate zooplankton composition, including microzooplankton, copepod nauplii, as well as small and large copepod ... -
Zooplankton excretion metabolites stimulate Southern Ocean phytoplankton growth
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2017-04-24)Warming over Antarctica is leading to changes in the zooplankton communities inhabiting the Southern Ocean. It has been observed that zooplankton not only regulates phytoplankton through grazing, but also through the recycling of nutrients that are essential for phytoplankton growth. In this way, the effects of warming on zooplankton populations will change the amount or proportion at which recycled ...


 English
English norsk
norsk